Amplitude Modulation (AM):
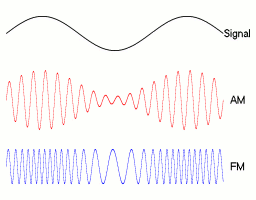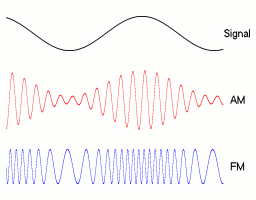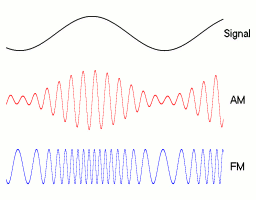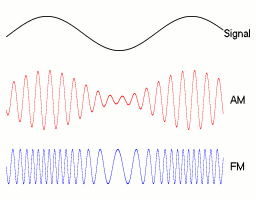
Amplitude Modulation (AM) is a method of impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) carrier waveform. The highest frequency of the modulating data is normally less than 10 percent of the carrier frequency.
Applications:
- Broadcast transmissions: AM is still widely used for broadcasting on the long, medium and short wave bands.
- Air band radio: Very High Frequency transmissions for many airborne applications still use AM. It is used for ground to air radio communications as well as two way radio links for ground staff as well.
- Single sideband: AM in the form of single sideband is still used for High Frequency radio links.
- Quadrature AM: AM is widely used for the transmission of data in everything from short range wireless links such as Wi-Fi to cellular telecommunications and much more.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| It is simple to implement | An AM signal is not efficient in terms of its power usage. |
| It can be demodulated using a circuit consisting of very few components. | It is not efficient in terms of its use of bandwidth, requiring a bandwidth equal to twice that of the highest audio frequency. |
| AM receivers are very cheap as no specialised components are needed. | An AM signal is prone to high levels of noise because most noise is amplitude based and obviously AM detectors are sensitive to it. |
Frequency Modulation (FM):
FM is a method of impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave.
Types of FM:
- Narrow band FM: For radio communications, a lesser bandwidth turns out to be the most feasible. These FM waves have deviation of less than ±3 kHz.
- Wide band FM: Broadcast stations that transmit in the Very High Frequency range of the spectrum between 88.5 and 108 MHz use a typical deviation of ±75 kHz.
Applications:
- FM Radio: FM radio uses a modulation index, m>1 and this is called wideband FM.
- Television sound
- Satellite TV: Some satellite TV transmissions broadcast an analogue video signal using FM.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Amplitude of the frequency modulated wave remains unaffected. | FM wave cannot cover large area. |
| Noise may reduce by increasing deviation. | Transmitting and receiving equipments for FM are complex and costly. |
| Operate in Very High Frequency. | A much wider channel, typically 200kHz, is needed for FM. |
Difference between AM and FM